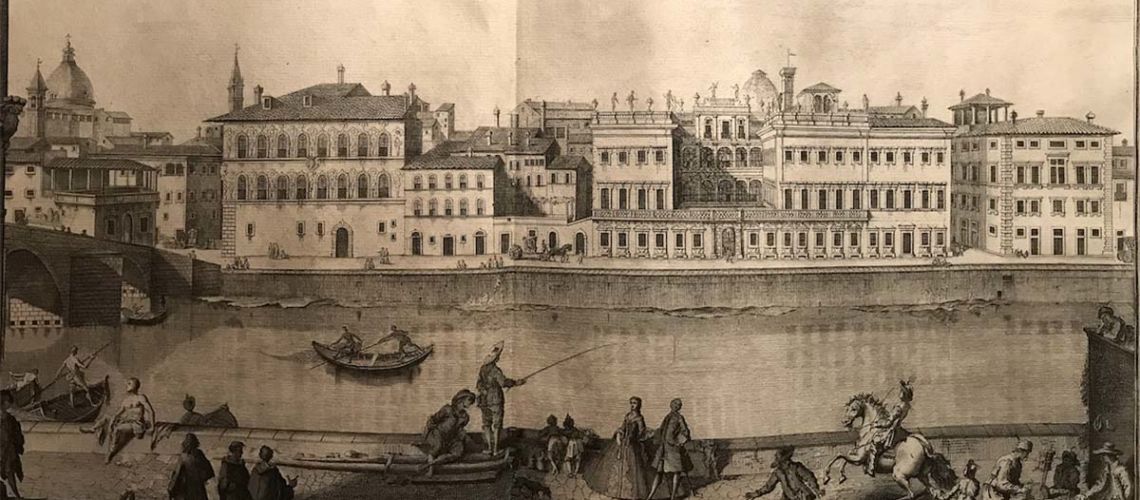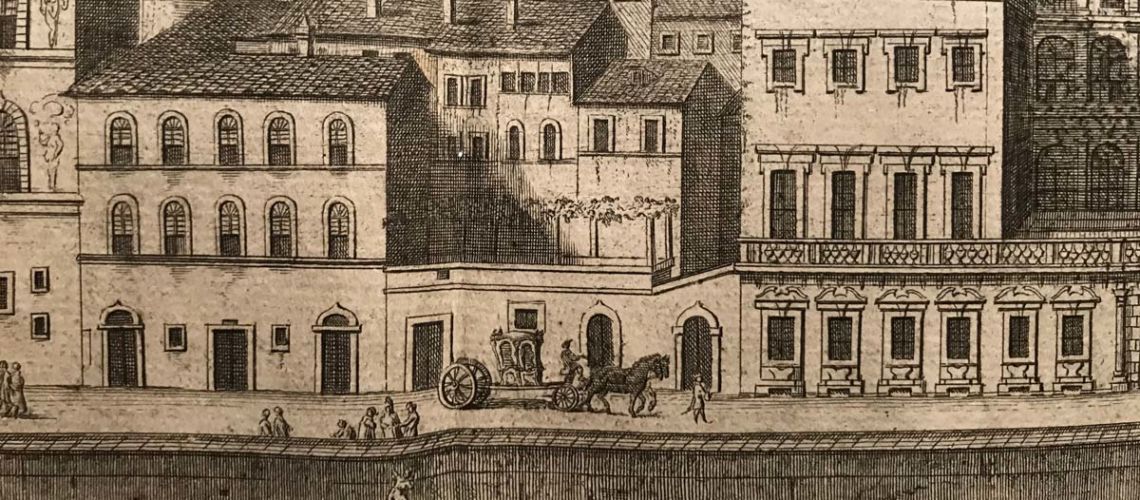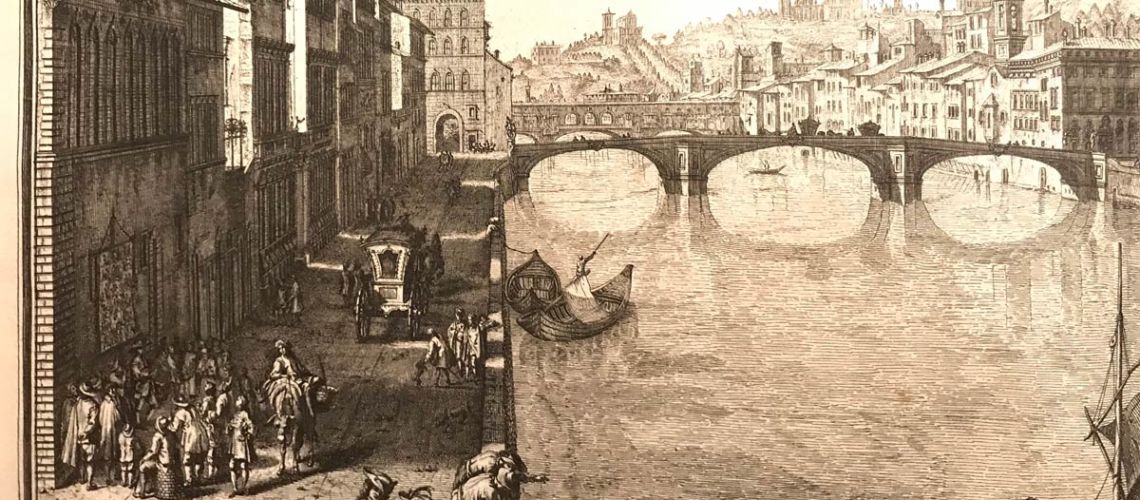Lungarno Corsini and Galleria Bazzanti
First Part
Roman Florence
Florence, a Roman city founded in the 1st century BC, had its brick walls with a defense moat, obtained by moving the Mugnone river along them, that is to say in the current Via Tornabuoni, which currently ends in Lungarno Corsini. The walls continued to be used and maintained until after 1000 AD. In 1078 they were enlarged only towards the Arno river to incorporate the new suburbs born on the banks of the river. In those times the Galleria Bazzanti had not been opened yet!
Florence in the Middle Ages
XII Century was a century of great population growth, and the suburbs continued to spread outside the walls, so much so that in 1172 it was decided to build new stones walls considerably larger that would incorporate them. To create the defense moat, the Mugnone river was moved again, making it unload in the Arno in the current Goldoni square. It is at this time that the bank of the Arno is reclaimed, and that the road along the Arno that will become the Lungarno Corsini is born. In this century of great building expansion, buildings were built throughout the area included in the new walls; the road that later became the Lungarno Corsini, future location of the Galleria Bazzanti, bordered the river on the west side of the Borgo district, where some Florentine families had land and buildings
The oldest "portraits" of Florence and the Lungarno Corsini
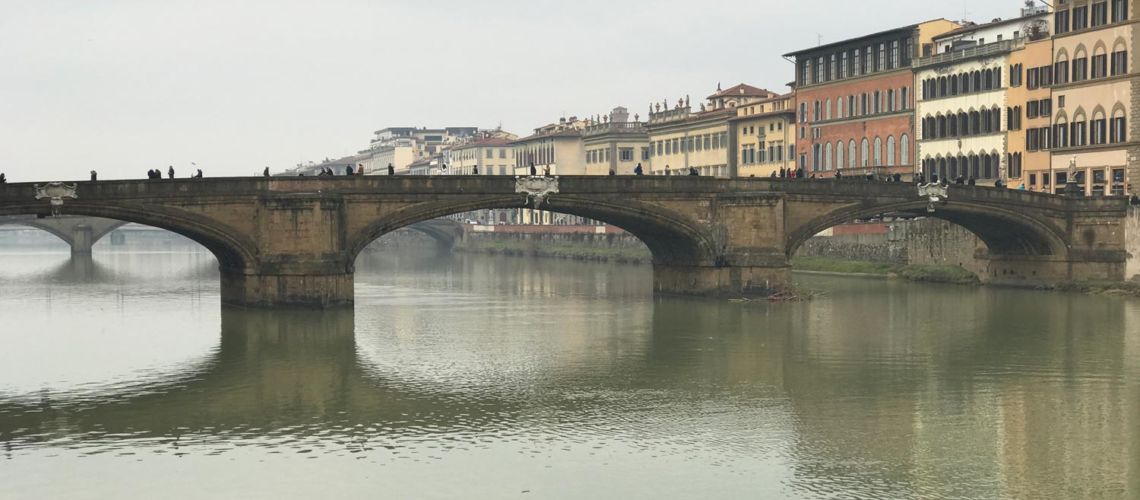
The Lungarno Corsini is that stretch on the right side of the Arno river that goes from Santa Trìnita bridge
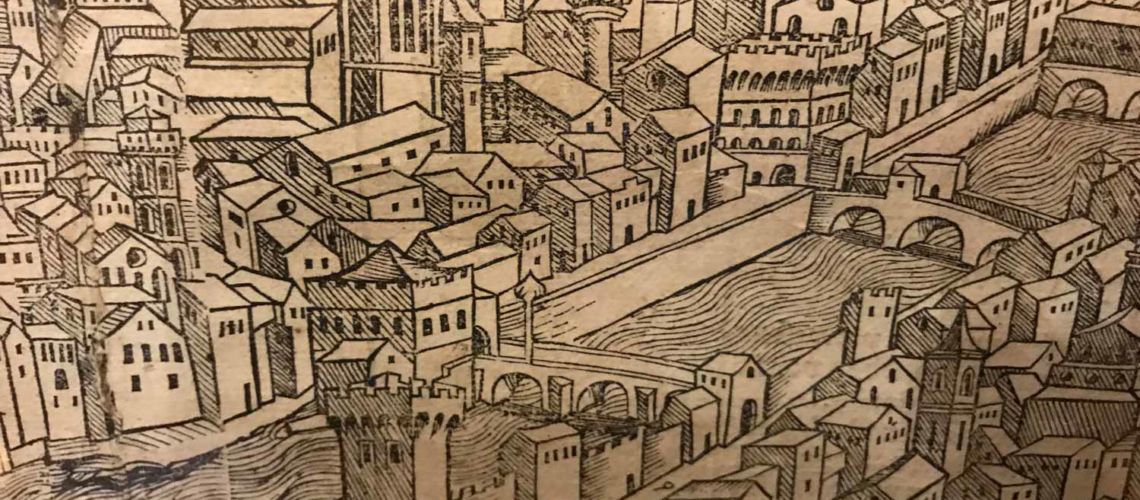
to Alla Carraia bridge. Both bridges were rebuilt in their original form after the destruction of the German troops in the last war. The first printed views of Florence date back to the second half of the fifteenth century; the most famous is the Berlinese view called “della Catena” which dates back to around 1470; It is printed on six sheets, and is in the Prints Cabinet of the Berlin Museum.
There are others of the late fifteenth century, the best known of which is the so-called “Schedeliana view” which is part of the H. Schedel Liber Chronicarum printed in Nuremberg in 1493.
In both we see how the future Lungarno Corsini is bounded to the right of the crenellated Feroni-Spini palace built at the end of the 13th century in correspondence of the Santa Trìnita bridge, and to the left from Ricasoli palace, (wrongly located inside the river and beyond Ponte alla Carraia in the Schedeliana view). We can also see how the Lungarno did not continue beyond the Carraia bridge. Also interesting is the Ghirlandaio fresco in the Sassetti Chapel of Santa Trìnita Church painted in 1475 with the stories of St. Francis: in the Miracle of the resurrected boy we can see the church of Santa Trìnita in that time, the fourteenth-century Carraia bridge and, to the right, the beginning of the Lungarno.
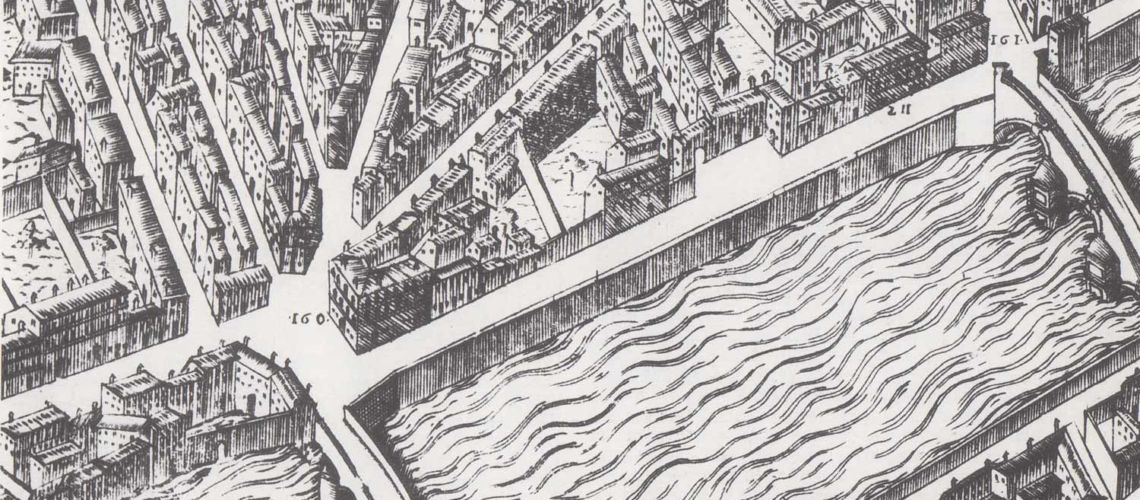
The first “scientific” view of Florence is the “Buonsignori” one of 1594
in which the houses of the Gianfigliazzi correspond to the number 211, while at n. 160 is the Ricasoli building. Halfway across the square is the piazza Gianfigliazzi which, through an archway, gave access to Via della Fonte (today via del Parioncino); this space was later occupied by the construction of a building for the enlargement of the Vallombrosian monastery of Santa Trìnita designed by Michelozzo with the central “Flemish” window.
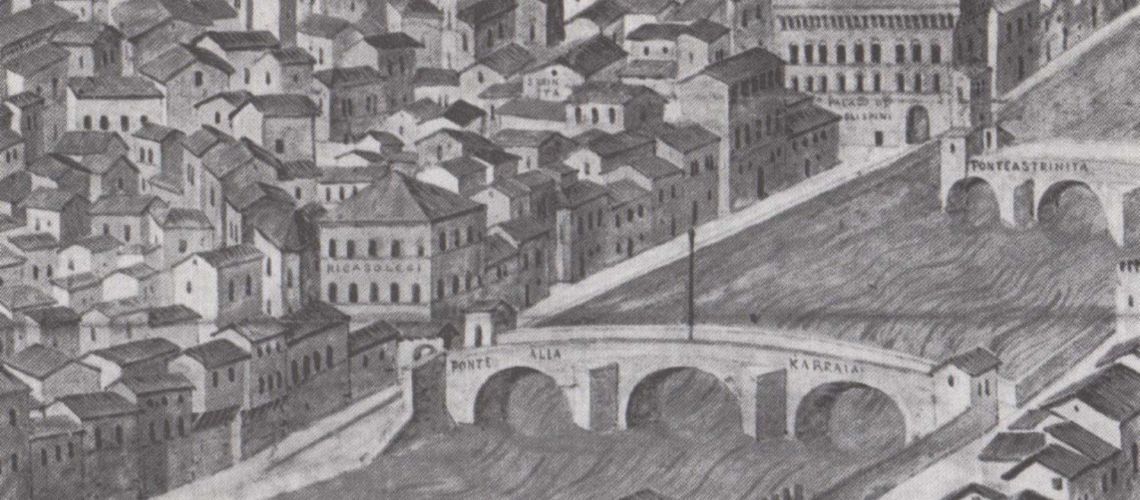
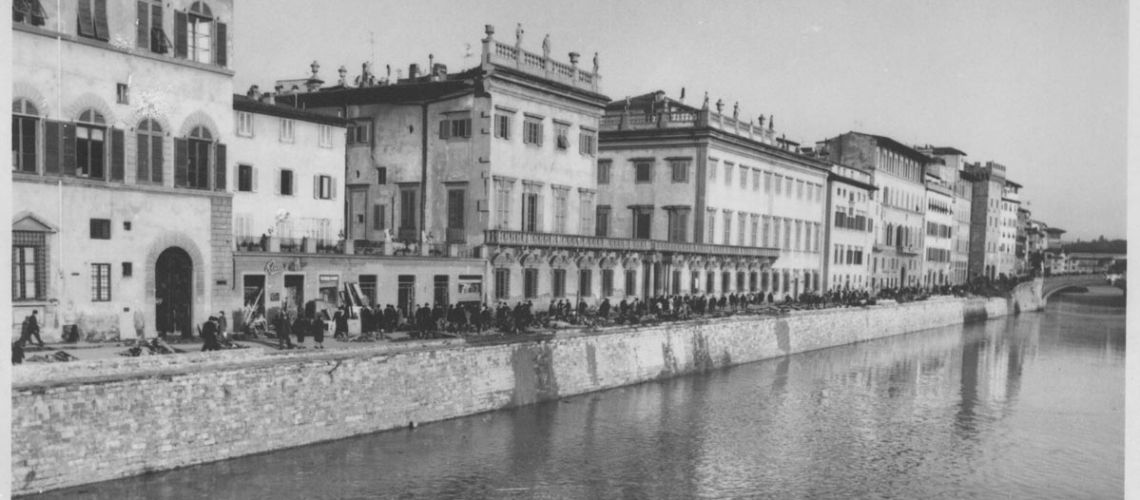
We can also see how the Lungarno ended with the Ricasoli palace and the Alla Carraia bridge. It will be continued with the construction of the “Lungarno Nuovo” in 1870. The widest part of the trapezium-shaped area was owned by the “Compagni” family up to the transverse wall that divided their garden from that of the Ricasoli family. We can see the large houses of the Compagni on Via del Parione dismantled and partly incorporated into the back of the Corsini palace near by the back entrance of the Galleria Bazzanti.
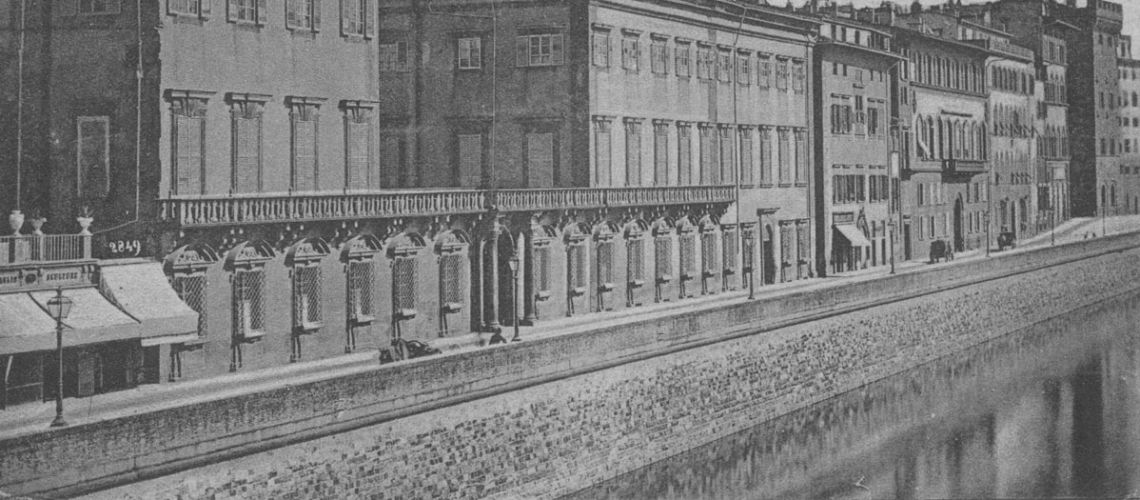
The Lungarno Corsini. prints, views, postcards
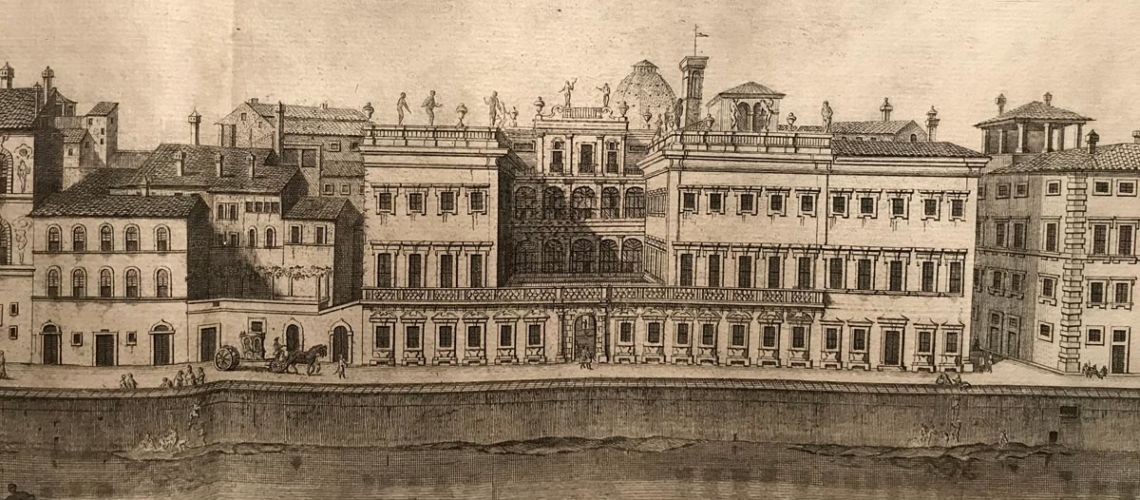
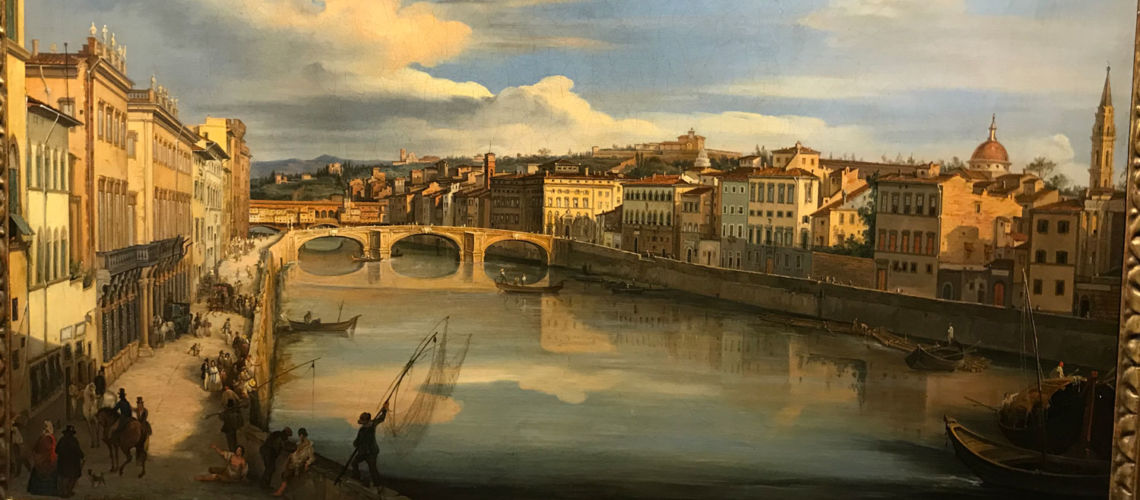
As soon as you enter the Galleria Bazzanti, you can see a print of Palazzo Corsini hanging: the most ancient views of the Lungarno are the large engravings of the Zocchi of about 1740.
In the first figure you can see the western part of the Lungarno, with the Cosini palace in the center and its left terrace (in front of which a horse carriage passes), then immediately before the Carraia bridge the Ricasoli Palace, and on the extreme right the house of the Vallombrosani with the large cross window, work of Michelozzo Architect, that has taken the place of the ancient square Gainfigliazzi. the other two figures are enlargements of a part of the Zocchi’s engraving showing the Corsini palace and the three doors and a window under the terrace, where the study of stone and marble sculpture was placed and that in the 19th century became the Galleria Bazzanti.
In another Zocchi’s engraving the foreshortened view of the Lungarno towards the Santa Trìnita bridge; on the left, after the Ricasoli palace, we see the three doorways and window under the Corsini terrace (with the same carriage passing in front of it), then the Corsini palace. Curious as the Lungarno in the direction of the Old Bridge (Ponte Vecchio), at the height of the S. Trìnita bridge, it passed under an arch of the Spini Feroni palace (then Ferragamo), which no longer exists.
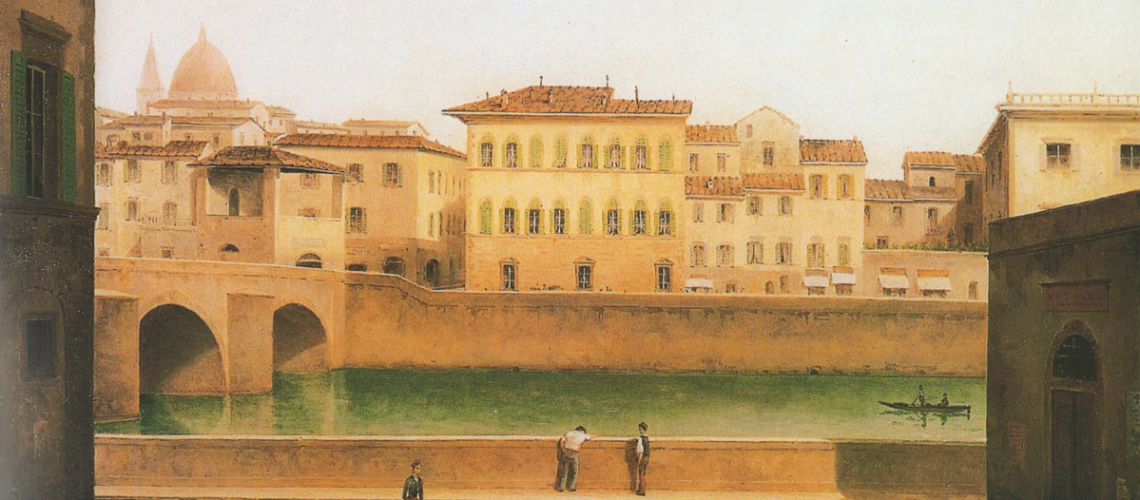
Of the early 19th century is a painting by Fabio Borbottoni where on the right you can see the Corsini terrace with under two openings and the curtains of the sculpture studio and Galleria Bazzanti, and a view of Lungarno Corsini by Giovanni Signorini of 1846 (detail).
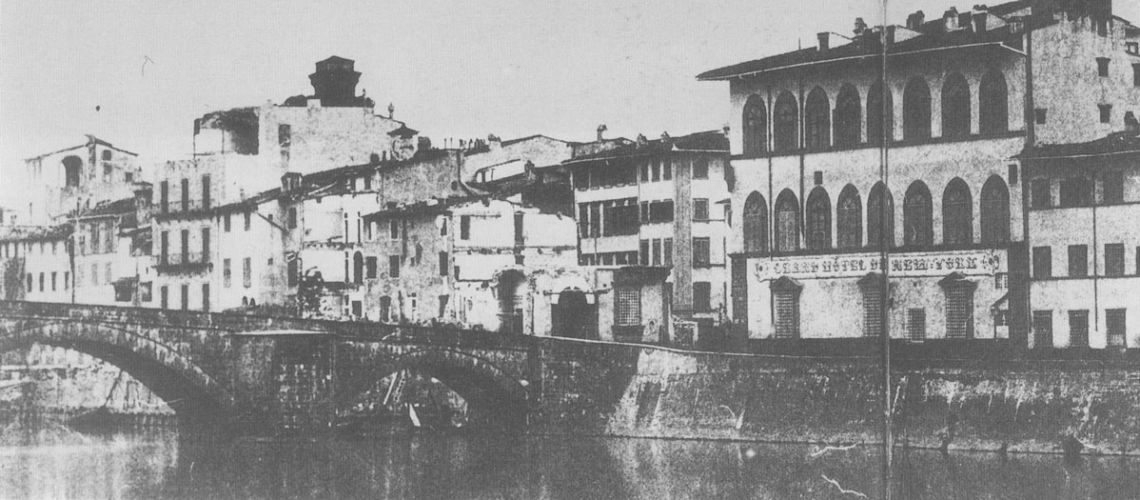
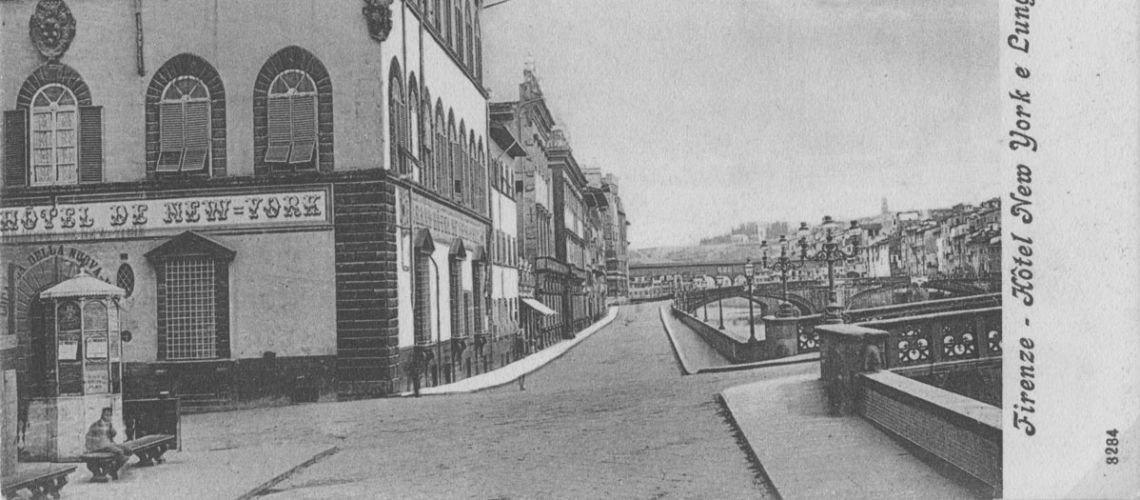
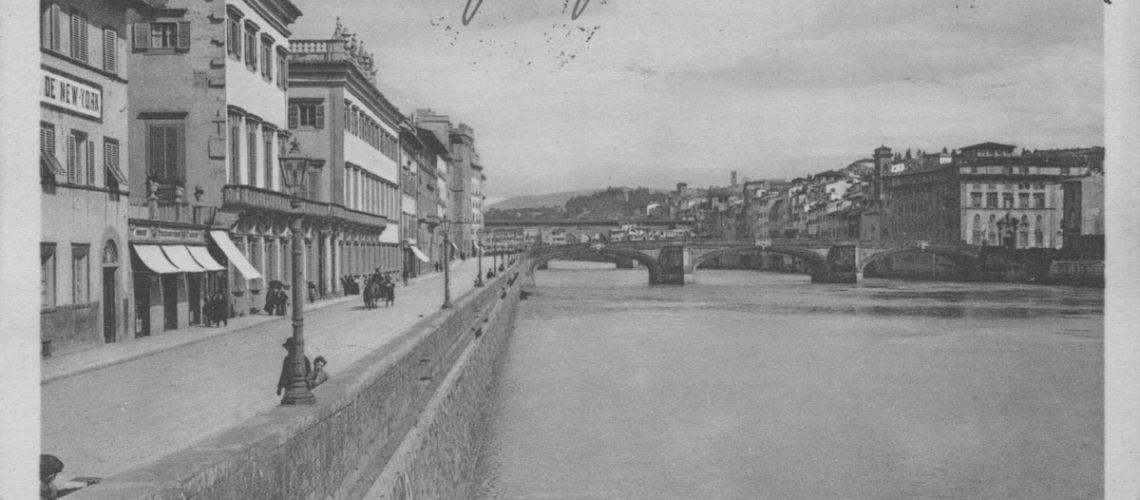
In the mid 19th century photo the end of the Lungarno Corsini appears with the Ricasoli building transformed into the New York Hotel (it had been Hotel since the second half of the 18th century under the names of “The English House” and then “Hotel du Nord”) and, beyond the Alla Carraia bridge, the beginning of the demolitions for the opening of the Lungarno Nuovo.
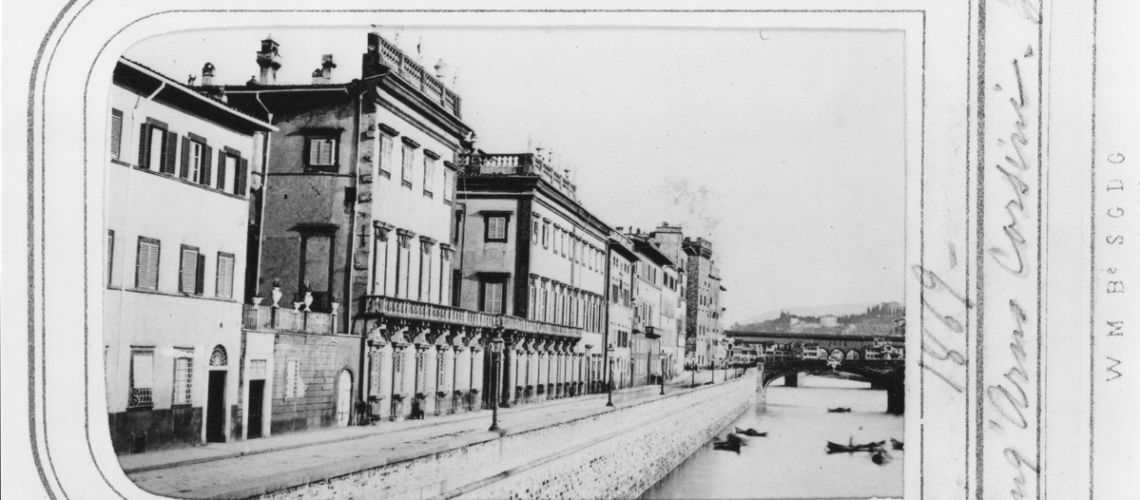
A photo from 1869 tells us that of the three doors of the sculpture studio existing in the 18th century under the terrace, one was closed, and the window enlarged.
In the last part of the 19th century there was a significant architectural change: the Ricasoli palace was laterally extended: in fact, on the Lungarno two more windows appear, which from 8 (first picture) become 10, and a second lateral entrance is created decentralized (second picture), to the detriment of a part of the adjacent building.
For some years nothing changed, with the exception of the curtains in the Galleria Bazzanti and the fact that the reduced construction became part of the New York Hotel.
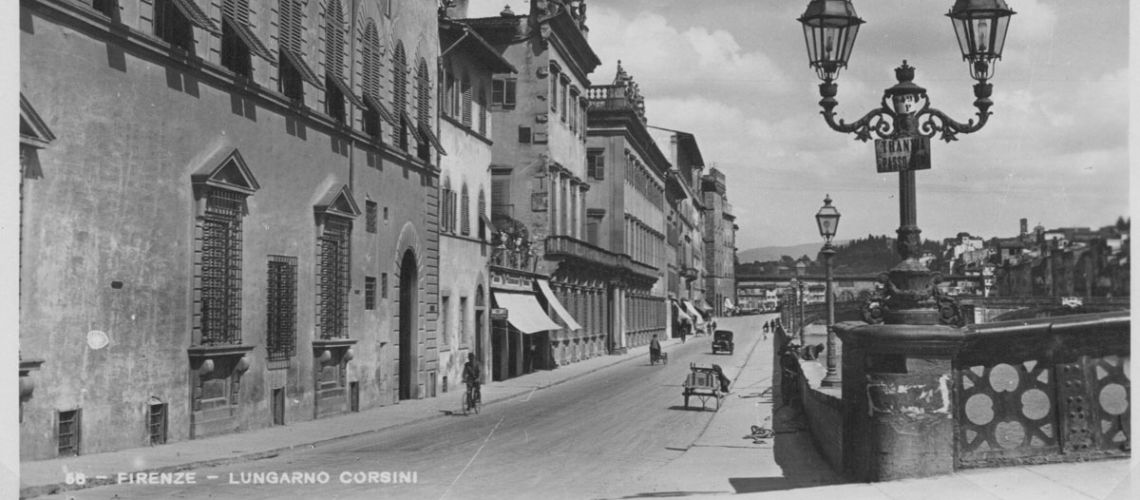
During the 20th century, a further architectural change brought the building adjacent to the Ricasoli palace back, allowing the extension of the terrace and the creation of other shops with other doors.